 |
Chart Types A list of available chart types |
Chart Types
To access this dialog:
-
Activate the Optimization ribbon and select Charts | Type.
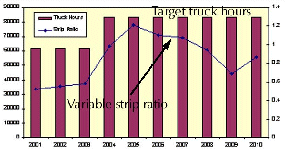
The following chart types are available for selection:
Line: a line connecting the data points of a variable.
Line with points: a line connecting the data points of a variable, the data points are covered with widgets.
Step: a graph similar to a Line graph except that horizontal and vertical line segments (forming a step) connect the data points of a variable.
Step with points: a step graph with data points covered by widgets.
Area under curve: a graph similar to a Line graph except the area below the data line is filled. If more than one variable are plotted, they are drawn in order of decreasing average value so that the variables with smaller values are not obscured by the variables with larger values
Strata: a graph similar to an Area graph, but it shows the summed total of a particular index over all variables. The height of the combined area represents the total over all variables. Sub-areas show how much each variable contributes to the total.
Vertical bar: a graph where the data values are indicated by the vertical extent of individual rectangles.
Extended vertical bar: a vertical bar graph that gives the bars and axes a 3D look.
Stacked vertical bar: the length of the combined bar represents the total over all variables. Areas within the bar show how much each variable contributes to the total
100% Stacked vertical bar: a graph similar to a bar graph, except all the combined bars have the same height. Like a Pie graph, the relative importance of the contributing factors is displayed. These graphs highlight the variation of these contributions over time or place. In this style, a bar is drawn for each index with segments showing the relative contributions of each variable. Because negative values can not be represented, a standard bar chart is drawn if the data contain negative values
Manhattan (IsoBar): a graph that represents data values as a three-dimensional rectangle. The chart resembles the Manhattan skyline. Because negative values can not be represented, a standard bar chart is drawn if the data contain negative values.
Rooftop (IsoArea): a graph similar to an IsoBar graph except the “roof top” between data values comprises sloped surfaces rather than steps. No lines are drawn to separate the indices. Because negative values can not be represented, a standard bar chart is drawn if the data contain negative values.
Ribbon: a graph similar to an IsoArea graph except just the “roof top” is drawn, without any sides. Because negative values can not be represented, a standard bar chart is drawn if the data contain negative values.
|
|
Related Topics |
|
|
Copyright © Datamine Corporate Limited
JMN 20065_01_EN